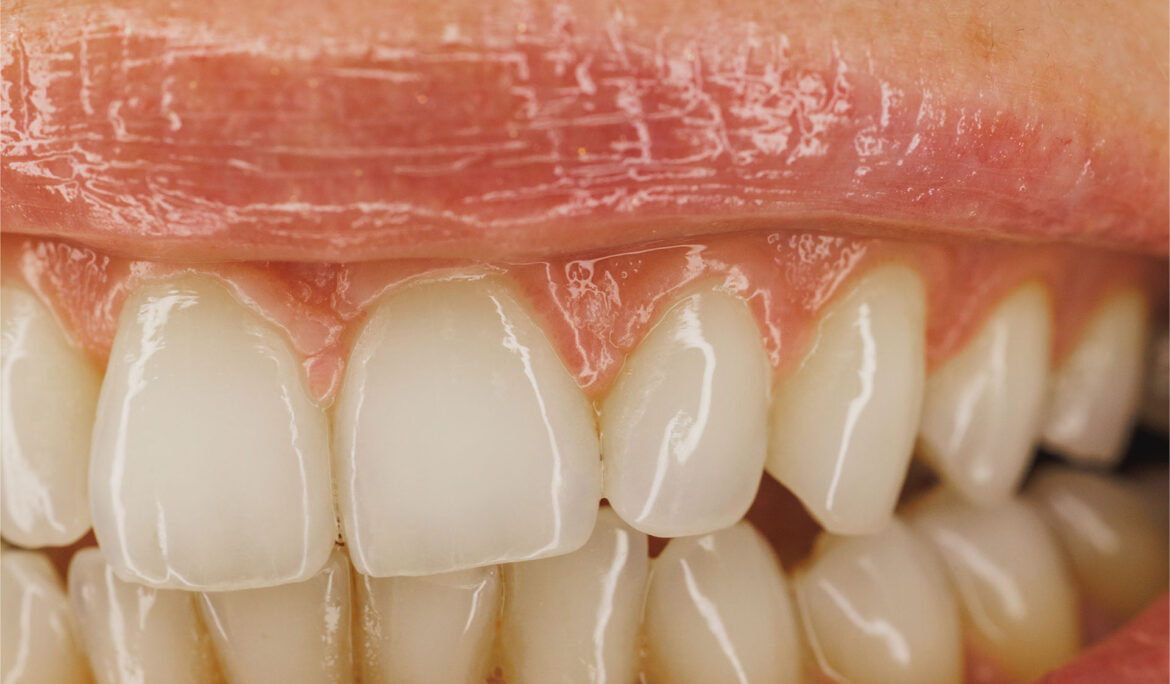
Inflammation of the gums, also known as gingivitis, is a common condition that affects almost the entire adult population. It is characterized by redness around the teeth and bleeding gums, which become painful.
The primary cause of gum inflammation is inadequate oral hygiene, resulting in the accumulation of plaque on the teeth. Over time, this plaque can harden into tartar, exacerbating the inflammation. If not removed promptly by a dentist, the inflammation can spread to deeper structures of the tooth-supporting apparatus, leading to bone resorption and gum recession.
Therefore, it is crucial to remove plaque through daily brushing and regular tartar removal during dental visits.
In addition to oral causes, systemic factors such as smoking, weakened immune system, diabetes, and hormonal changes can contribute to gum inflammation. In such cases, maintaining good oral hygiene becomes even more critical for gum health.
Gingivitis primarily affects the gum tissue, causing inflammation and redness, especially at the gum line. If left untreated, it can progress to bleeding gums and swelling. Without intervention, the inflammation can extend beyond the gum tissue, affecting the supporting structures of the teeth and leading to bone resorption and gum recession.
Treatment of gum inflammation focuses on proper oral hygiene. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and toothpaste formulated for gum health is recommended. Additional products such as gels may help soothe the gums. Dental floss and, if applicable, oral irrigators can also improve oral hygiene. Electric toothbrushes designed for sensitive gums can be beneficial.
The duration of treatment varies but typically lasts one to two weeks after implementing proper oral hygiene and, if necessary, professional tartar removal.
Preventing gum inflammation involves:
- Brushing teeth at least twice daily
- Using toothpaste formulated for gum health
- Regularly replacing toothbrushes
- Using dental floss and, if applicable, oral irrigators
- Visiting the dentist every six months.